Do you ever find yourself struggling with Data Transcription? Unsure about what it is and how it can benefit you? Don’t worry, you’re not alone! This guide will demystify the world of data transcription. From understanding the different types of data transcription to exploring the challenges it poses, we’ve got you covered. So, get ready to unlock the secrets of it and take your skills to the next level!
Table of Contents
What is Data Transcription?

Data Transcription refers to the process of converting various forms of data into written or textual format. It involves taking information from sources like audio recordings or images and converting them into text-based formats. By transcribing data, we create readable and searchable documents that can be easily analysed, shared, and stored. This enables efficient data management, retrieval, and analysis, aiding in tasks such as research, data processing, and information organisation. It plays a vital role in industries like healthcare, legal, market research, and media, where accurate and reliable textual representations of data are essential for decision-making and analysis.
Types of Data Transcription
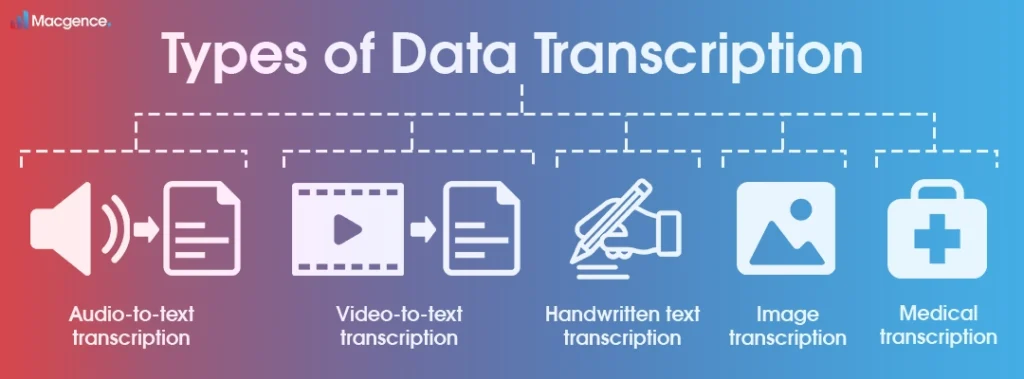
Different types of Data Transcription include:
- Audio-to-text transcription: It converts spoken language from audio recordings into written text. Additionally, it can be used for transcribing interviews, podcasts, dictations, and other audio content.
- Video-to-text transcription: It converts spoken words or dialogues from video recordings into text format. Moreover, it’s useful for transcribing videos, webinars, presentations, and other content.
- Handwritten text transcription: It transforms handwritten documents into typed or digital text, thus enabling easier access, editing, and storage of handwritten information.
- Image transcription: Extracts textual information from images. It can be used to transcribe text from scanned documents, signs, labels, etc.
- Medical transcription: Converts medical records, patient notes, or doctor’s dictations.
Each type of transcription serves a unique purpose, thereby facilitating data management, analysis, and accessibility across a range of contexts and industries.
Tools and Techniques for Data Transcription

Let’s explore the tools and techniques used for transcription:
- Manual Transcription: It typically involves a human transcriber listening to the audio or watching the video and manually typing the spoken words or content into written form. It ensures accuracy and also allows for contextual understanding.
- Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR): Utilises advanced algorithms to automatically convert spoken language into text by analysing audio input and detecting speech patterns. It enables fast transcription but may require post-editing for accuracy.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): It applies pattern recognition and machine learning to recognize and convert printed or handwritten text from images or scanned documents into editable digital text. Consequently, it facilitates the transcription of printed materials and speeds up the process.
- Handwriting Recognition: Utilises machine learning algorithms to analyse and recognise handwritten text, converting it into digital text format. It specifically enables the transcription of handwritten documents, notes, and forms.
- Image Transcription Tools: It employs specialized software or platforms that extract text from images using OCR techniques, thereby enabling the transcription of textual content present within the images. Moreover, it allows for the transcription of text in scanned documents, photographs, or screenshots.
These techniques provide different approaches to transcription, thereby catering to various requirements and scenarios. Additionally, they combine human effort, advanced algorithms, and specialized tools to convert audio, video, and image data into written text, thus facilitating efficient data management, analysis, and accessibility.
Benefits of Data Transcription
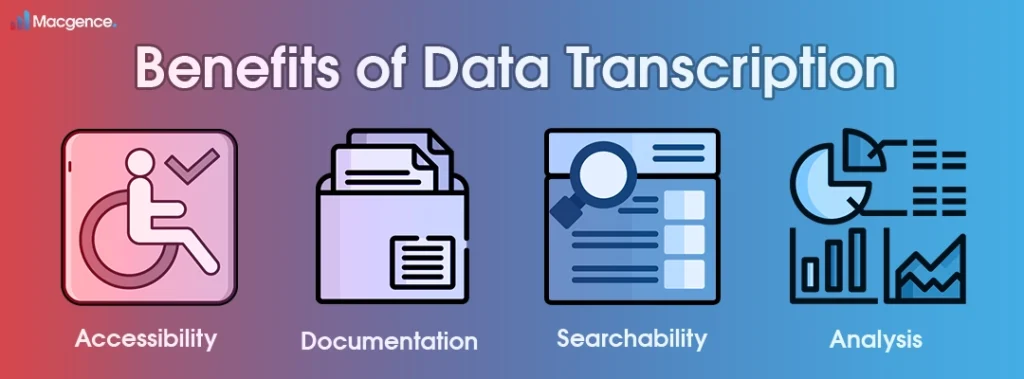
Transcription offers numerous benefits in various industries and contexts. Let’s look at some key advantages:
- Accessibility: Transcribing data further makes it accessible to individuals with hearing impairments or language barriers, ensuring that everyone can engage with the information.
- Documentation: Transcriptions create a written record of important conversations, interviews, or events, therefore serving as a reliable resource for future use.
- Searchability: By converting audio or video content into written text, transcriptions significantly enable easy search and retrieval of specific information, saving time and effort.
- Analysis: Written transcriptions undoubtedly facilitate detailed analysis of data, allowing researchers, analysts, and professionals to extract insights, identify patterns, and make informed decisions.
Challenges in Data Transcription

Transcribing data comes with its fair share of challenges. For instance, one such challenge is dealing with different accents and dialects, which can affect the accuracy of automatic transcription systems or require specialized knowledge from human transcribers. Background noise in audio recordings is another hurdle, as it can make it difficult to accurately capture and transcribe the intended speech.
Identifying speakers and managing overlapping speech poses additional difficulties. When multiple speakers are involved, or conversations overlap, accurately assigning the spoken words to the correct individuals becomes crucial.
Handwritten text transcription presents its own set of obstacles. Specifically, poor handwriting legibility and variations in writing styles can make it challenging to interpret and transcribe handwritten documents, notes, or forms.
Furthermore, incomplete or damaged data sources can complicate the transcription process. Whether it’s distorted audio, partially visible text, or low-quality images, such data can lead to missing or inaccurate transcriptions. Transcribers should handle such data with care and may need to intervene manually to fill in gaps and ensure transcription accuracy.
Conclusion
In summary, It is important for converting valuable information into a format that is easy to work with. Throughout this guide, we have covered different types of data transcription, the challenges you may encounter, as well as the useful tools available to make the process smoother. We hope that you now feel more confident in tackling transcription tasks. And when you need top-notch Data Transcription Services, remember that Macgence is here to assist you.
Get started with Macgence
As a leading company in the field of transcription, Macgence can assist you with a wide range of transcription needs. We take pride in offering 100% human-generated data transcription solutions, ensuring that your transcriptions are handled by skilled human transcribers rather than relying solely on automated processes. With proficiency in over 150 languages, our team can efficiently handle transcription requirements for clients worldwide, providing accurate and reliable transcriptions in diverse languages. Moreover, our extensive network comprises over 10,000 experienced transcribers who are dedicated to their craft. When you choose Macgence, you gain access to reliable and efficient transcription solutions tailored to your specific needs.




