- What basically is meant by LiDAR?
- The Significance of LiDAR for Autonomous Vehicles
- The Operation of LiDAR in an Autonomous Vehicle
- LiDAR Comparison with the Other Present Sensing Technologies
- Limitations and Difficulties with LiDAR
- LiDAR-equipped vehicles' benefits for the environment
- The Future of LiDAR in Autonomous Driving
- Conclusion
How LiDAR In Autonomous Vehicles are Shaping the Future
Have you ever wondered how autonomous vehicles determine when to merge, stop or be clear of obstacles? It is all a result of intelligent technologies, of which LiDAR is a major participant. Imagine it as an autonomous car’s eyes. LiDAR creates a very comprehensive 3D map by scanning the area surrounding the automobile using laser light. The car can “see” what’s going on on the road in real time thanks to this. This blog post will explain LiDAR’s definition, operation, and significance for the development of autonomous vehicles.
What basically is meant by LiDAR?
It represents Light Detection and Ranging. This remote sensing technique measures distances with remarkable accuracy using laser light. LiDAR is a high-tech echolocation system that employs light, much way bats do with sound waves, to sense their environment.
This is how it functions: Thousands of laser pulses are sent out every second by a LiDAR system. After bouncing off things like vehicles, trees, structures, or people, these pulses return to the sensor. By tracking the time it takes for each pulse to return, the system calculates the exact distance to each item.
The Significance of LiDAR for Autonomous Vehicles
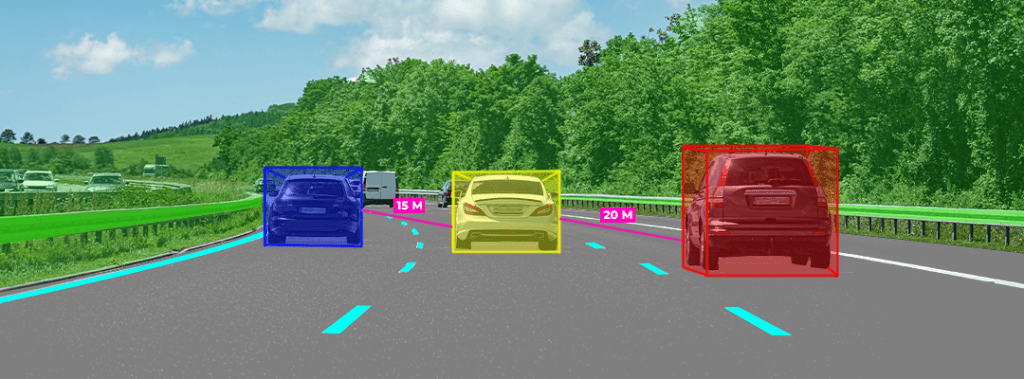
It is essential to the precise and safe navigation of autonomous vehicles. This is why it’s such an important component:
Creates a 3D map of the surroundings
- Uses laser pulses to scan the environment
- Builds a real-time, detailed view of roads, objects, and terrain
- Accurately detects obstacles
- Spots vehicles, roadblocks, potholes, traffic cones, and other hazards
- Helps the car slow down, stop, or change course as needed
- Identifies pedestrians and animals
- Tracks movement with precision
- Enhances safety in areas with foot traffic or unexpected crossings
- Recognizes road features
- Detects lane markings, curbs, road edges, and elevation changes
- Assists in staying centered within lanes and handling turns
- Performs well in various lighting conditions
- Functions reliably in bright sunlight, total darkness, or low-visibility environments
- Not affected by changes in natural light like a standard camera might be
- Provides consistent, real-time data
- Enables fast decision-making by the vehicle’s onboard system
- Reduces the chance of errors caused by sudden environmental changes
It serves as autonomous cars’ sense of vision, providing precision and dependability in circumstances when safety is crucial.
The Operation of LiDAR in an Autonomous Vehicle
Being more than simply a sensor, It is crucial to how autonomous vehicles perceive and interact with their environment. Each stage contributes to safe and intelligent navigation, from the device’s placement on the vehicle to its interactions with other systems.
Sensors mounted on the car
In order to provide optimal coverage, LiDAR sensors are positioned strategically throughout the vehicle. The location varies according to the design of the car, but typical locations are the sides, bumpers, front grille, and top.
- 360-degree views of the environment are provided by LiDAR installed on the roof.
- Sensors on the front and sides improve near-range detection and assist in covering blind spots.
- Compact, solid-state sensors are used by certain vehicles for seamless integration, whereas spinning LiDAR units are used by others for wider scans.
Data Gathering and Processing in Real Time
After mounting, quick bursts of laser light are released by the LiDAR system to start scanning the surroundings. The sensor can determine distance depending on the time it takes since these pulses bounce off surrounding objects and return.
- Each second, thousands of laser beams are released by the system.
- Every signal that is received aids in determining the precise form, location, and motion of nearby objects.
- The car can comprehend its environment in real time thanks to the instantaneous processing of all this data.
Connectivity to Other Systems
LiDAR is not an isolated system. It is a component of a wider network of technology and sensors that cooperate to steer the car.
- Traffic signs, signals, lane markings, and color distinctions may all be visually recognized by cameras.
- By monitoring objects over greater distances and in inclement weather, radar enhances LiDAR.
- Real-time safe driving judgments are made by AI and machine learning algorithms that evaluate input from all sensors.
LiDAR Comparison with the Other Present Sensing Technologies
A variety of sensor technologies are used by autonomous cars to travel safely. Despite its importance, it’s vital to know how the overall LiDAR system uses sensors like radar and cameras.
Comparing LiDAR and Cameras
Like human eyes, cameras are able to catch fine details in photographs. Reading traffic signs, seeing lane markings, and identifying traffic signals all depend on them. They do have certain restrictions, though:
- Strengths:
- Great for identifying colors, text, and visual cues
- High-resolution images provide detailed object recognition
- Weaknesses:
- Struggle in low light, glare, fog, or heavy rain
- Limited depth perception without complex algorithms
Comparison with Radar
It uses radio waves to detect objects and measure their speed and distance. It’s particularly useful for long-range detection and bad weather conditions.
- Strengths:
- Works reliably in poor weather and low visibility
- Can track the speed of moving objects
- Weaknesses:
- Provides lower resolution compared to LiDAR
- Less effective at detecting small or static objects
The Reasons for Using a Combination
Not all sensors are perfect. For this reason, most autonomous vehicles employ sensor fusion, a technology that integrates LiDAR, cameras, and radar.
- LiDAR provides 3D mapping and precise obstacle recognition.
- Cameras introduce color and visual recognition.
- Accurate speed and distance tracking is made possible using radar, especially in bad weather.
Limitations and Difficulties with LiDAR
Although this technology is helpful for autonomous vehicles, there are a lot of problems that need to be fixed before it can be applied more extensively. Here are six important limitations:
1. Expensive
Compared to other sensing technologies, sensors are more expensive. Because high-resolution components are expensive to build, automakers are having difficulty creating mass-market, affordable self-driving cars.
2. Sensitivity to weather
Unfavorable weather conditions might impact LiDAR’s functionality. Snow, fog, and precipitation can absorb or spread laser beams, making distance measurements less precise. As a result, the technology might not be as dependable in actual driving situations.
3. High Requirements for Data Processing
Massive amounts of real-time 3D spatial data are provided by LiDAR sensors. Advanced onboard processors are needed to process this data rapidly, which might raise the vehicle’s price and energy use.
4. Integration Challenges
Visible modules might have an impact on the vehicle’s aerodynamics and overall appearance. Without sacrificing functionality or aesthetics, manufacturers may find it difficult to incorporate large sensors into the present designs.
LiDAR-equipped vehicles’ benefits for the environment
1. Enhanced Route Scheduling
- Using real-time data, LiDAR-enabled cars can navigate and select the most efficient routes.
- This lowers the total impact on the environment, cuts down on travel distance, and decreases idle time in traffic.
2. Using Autonomous Shared Fleets to Cut Down on Urban Pollution
- Many LiDAR-equipped autonomous vehicles are a feature of ride-sharing companies.
- Because there are fewer privately owned vehicles on the road, traffic is less backed up, and noise and air pollution in cities are decreased.
3. Support for Electric Vehicle Integration
- LiDAR technology is often integrated into electric autonomous vehicles, which already produce zero tailpipe emissions.
- The combination helps promote the use of clean, intelligent transportation in both urban and highway settings.
4. Less Waste of Resources in Logistics
- LiDAR-enabled autonomous delivery trucks increase delivery efficiency and cut down on return trips.
- This contributes to more ecologically friendly logistics by using less gasoline and producing less packaging waste.
5. Better Urban Planning and Land Use
- LiDAR’s accurate mapping skills aid in the creation of more intelligent parking lots, city layouts, and roads.
- Effective land use promotes the growth of greener, more sustainable cities and lessens environmental harm.
The Future of LiDAR in Autonomous Driving
1. The Solid-State LiDAR’s rise
For scanning the surroundings, traditional LiDAR systems frequently employ spinning components; however, more recent solid-state LiDAR systems do not require moving elements. As a result, the sensors are easier to incorporate into cars, smaller, and more dependable. Solid-state LiDAR is anticipated to overtake other options for autonomous vehicle designs in the future because to its increased endurance and reduced cost.
2. Gradually Reduced Prices
LiDAR sensors are becoming more and more affordable as more businesses enter the market and output increases. This makes the technology more affordable for mass-market models as well as luxury cars. Reduced prices will play a major role in hastening the broad use of cars with LiDAR.
3. More Effectiveness and Performance
LiDAR systems of the future are being created with improved resolution, increased processing speed, and a greater range. These enhancements enable more accurate object detection and response by cars, especially in challenging situations or at faster speeds. Power consumption is also reduced by more effective systems, which enhances total vehicle performance.
5. Pervasive Use in All Industries
LiDAR is becoming more popular in sectors other than personal automobiles, such as agriculture, public transit, and logistics. It is helpful for autonomous farming equipment, self-driving vehicles, and delivery robots since it can offer accurate environmental data. The whole autonomous technology ecosystem stands to gain from this wider usage, which is expected to accelerate LiDAR development even further.
Conclusion
LiDAR is one of the most important instruments for self-driving automobiles to comprehend their environment. Vehicles can accurately identify road signs, pedestrians, and barriers because to the clear, real-time 3D model of the route it creates. Technology is advancing quickly, despite some obstacles like cost and weather. More cars are getting LiDAR systems that are smaller, more modern, and less expensive. LiDAR’s contribution to the safety, intelligence, and dependability of autonomous driving will only increase as these systems develop further. It’s genuinely advancing the direction of transportation in the future.
FAQs
Ans: – Although severe rain, fog, or snow can make LiDAR less effective, advancements in sensor design are assisting in easing these restrictions.
Ans: – While modern solid-state LiDAR systems are becoming more accessible and simpler to incorporate, classic LiDAR systems are still expensive.
Ans: – Most probable. Many autonomous systems are anticipated to use LiDAR as a crucial component as the technology becomes more affordable and smaller.
Ans: – Not by itself. In order to replace human driving abilities, LiDAR is a component of a bigger system that also consists of cameras, radar, and artificial intelligence.
Ans: – Very quick—LiDAR systems process data in real time to provide safe driving guidance while delivering thousands of laser pulses per second.
Ans: – No. LiDAR maps the environment by measuring distances and shapes; it does not take pictures or record personal information.
You Might Like
June 18, 2025
What is a Generative AI Agent? The Tool Behind Machine Creativity
In 2025, each nation is racing to build sovereign LLMs, evidenced by over 67,200 generative AI companies operating globally. The estimated $200 billion poured into AI this year alone. This frenzied investment is empowering founders of startups and SMEs. This assists the founders in deploying generative AI agents that autonomously manage workflows, tailor customer journeys, and […]
June 9, 2025
AI Training Data Providers: Innovations and Trends Shaping 2025
In the fast-paced B2B world of today, AI is no longer a buzzword — the term has grown into a strategic necessity. Yet, while everyone seems to be talking about breakthrough Machine Learning algorithms and sophisticated neural network architectures, the most significant opportunities often lie in the preparatory stages, especially when starting to train the […]
May 27, 2025
How Banking Data Annotation Is Transforming Financial Institutions
In the data-driven world of today, the banking and financial services industry is rapidly turning digital. Artificial intelligence (AI), from risk assessment and fraud detection to customized client experiences, is changing the way financial institutions function. However, data annotation serves as a vital basis for all intelligent systems. Because banking data is diverse, complicated, and […]




